MODERN SPACE

+breaks the “box” and lets the space flow
–horizontal connections
–vertical connections
CONTEMPORARY SPACE
+The entire building space is unique and continuous
+concept of FREE SECTION: ending the tyranny of the horizontal plane. Def.
CONCEPTS
+Composition: Action or effect of composing. Def.
+Rhythm: Sequence/repetition of shapes in space that sets the time. Def.
—ex) by separating windows in the wall, columns in a colonnade, pillars in an arcade
+Axis: Linear element that marks a direction and distributes the space or elements around it. Def.
+Symmetry: Regular arrangement of parts or points of a body or figure in relation to a centre, axle or plan. Def.

+Hierarchy: Relationship of supremacy of an element over others based on an established approach. Def.
–by the size/form/situation
+Module: A unitary element which serves as a proportional unit, and which is repeated on the same scale or at different scales. Def.
–Le Corbusier: system of proportions related to the human being, based on the golden ratio.

+Grid: Composition based on a grid of axes serving as a guide. Def.
+Movement: The irregularity of forms and the variants of order inspire the idea of movement, of displacement. Def.
.jpg?1384455904)

+Unity: The relationship of the parts to the whole so that nothing should be removed or added. Def.
— visual connection and looks like they belong together.
+Centrality: Organization of space around a center that creates attraction towards it. Def.
+Balance: Complementary relationship between the elements of a composition. Def.
–Static equilibrium: elements are equal and symmetrical
–Dynamic equilibrium: elements are compensated by geometric difference

Static 
Dynamic
+Limits: It is the edge of the elements of the composition where there is a change from the rest. Def.
+Light:
“Architecture is the learned game; correct and magnificent of forms assembled in the light. Our eyes are made to see the forms under the light: the shadows and the clearings reveal the forms“
— Le Corbusier
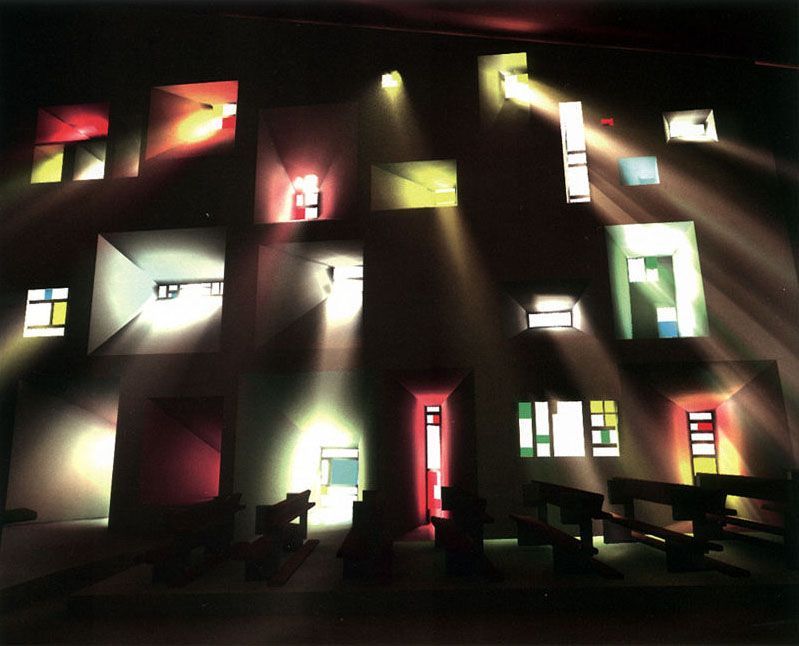
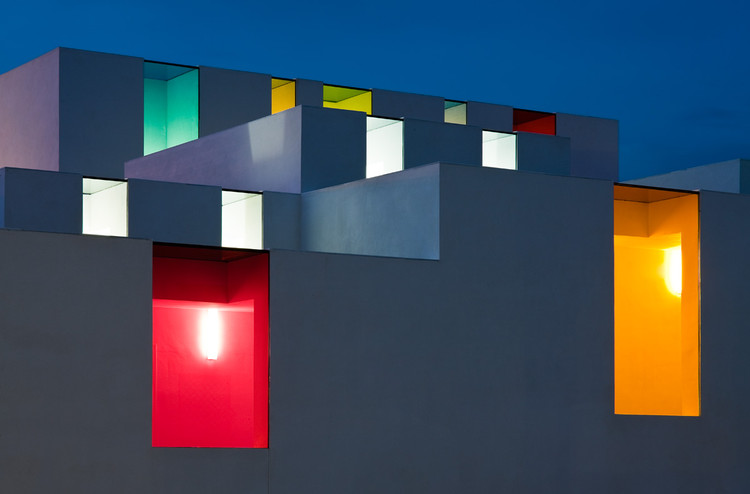



+Contrast: Chromatic manifestation of the elements to be used. Def.
+Colour: Chromatic manifestation of the elements to be used. Def.
+Texture: Surface finishing of the elements involved in the final perception of architecture. Def.
+Proportion: Harmonic relation of dimensions according to certain mathematical or geometric rules. Def.

Texture ex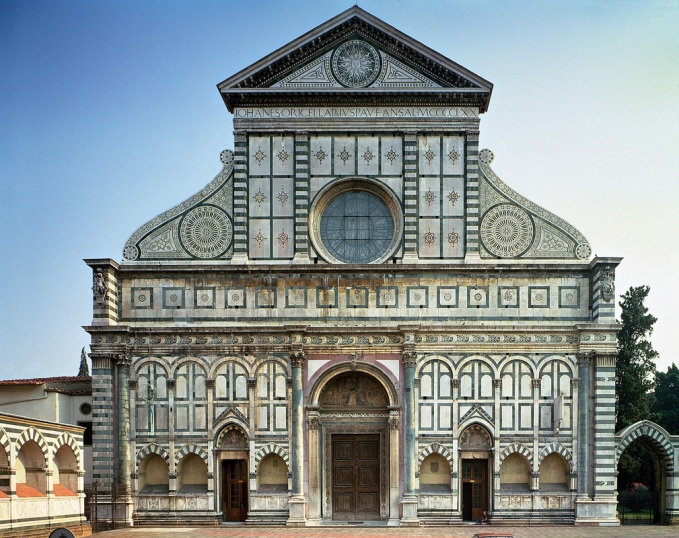 
Proportion ex
+Scale: Relation between the size of the building and the size of the human being.
Sizing referred to a selected unit. Def.
FUNCTIONALITY
Mechanical functionalism
-Began with the Industrial Revolution
Form follows function
Louis H. Sullivan
-Beauty comes automatically from the mechanical efficiency without looking for it.

+Moralistic Functionalism
-Beauty means precisely to make visible its utility (what it serve)
-something can be considered beautiful, when it is useful and suitable to its end
+Organic functionality
The form takes on a biological sense and adapts itself to the living functions which must be carried out in the architecture
Materiality
Construction techniques use the materials according to their qualities and properties —— artistic characteristics comes from that
+MATERIALS
-the shapes remain alive a even if architecture evolutes
-They are translated into new technological realities (ACCORDING TO SEMPER)
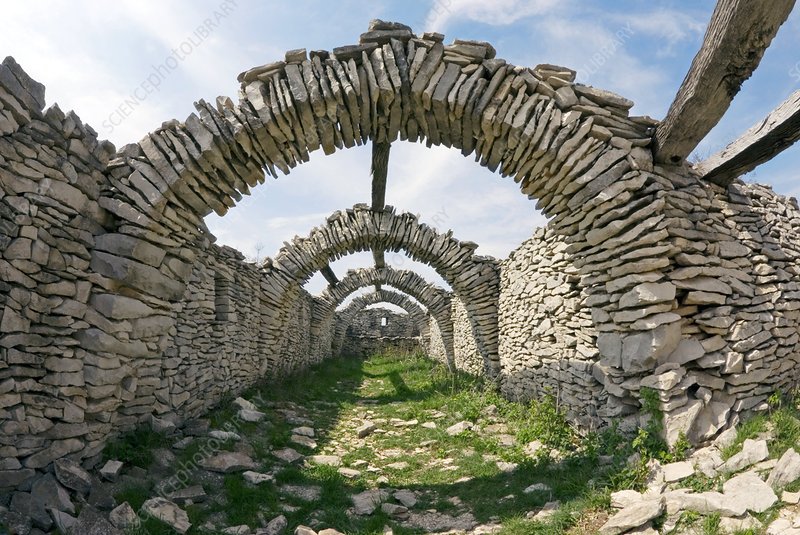

STONE. 
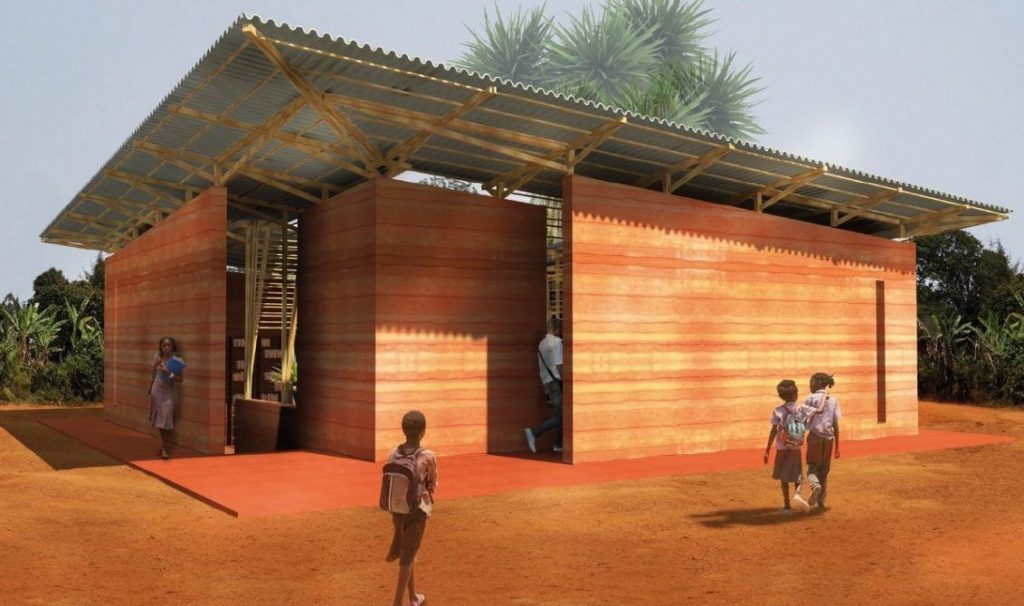

EARTH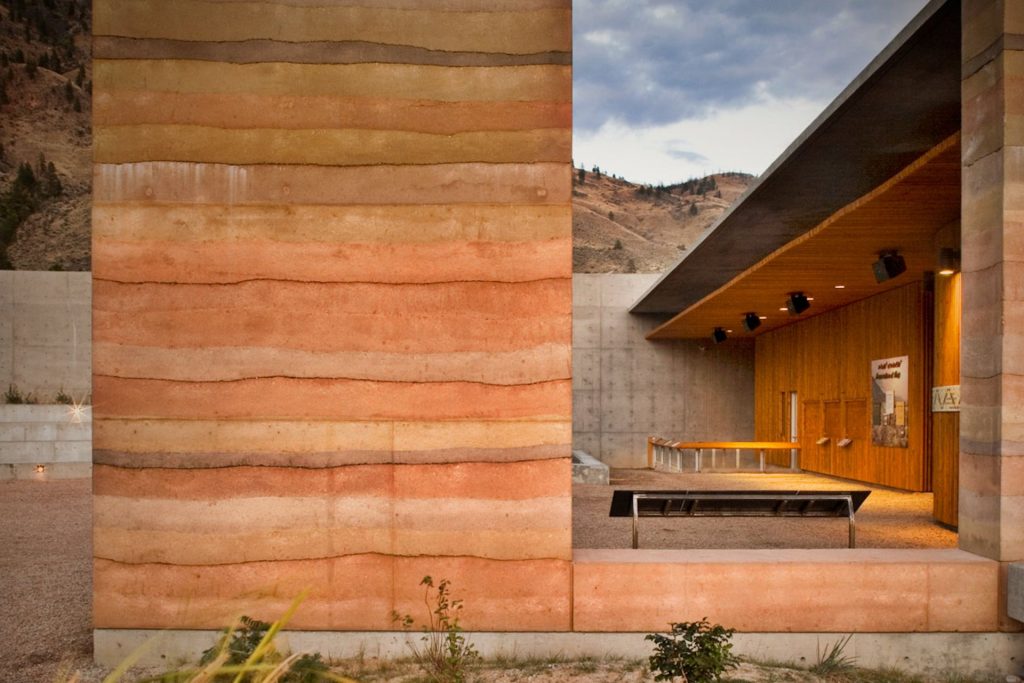 
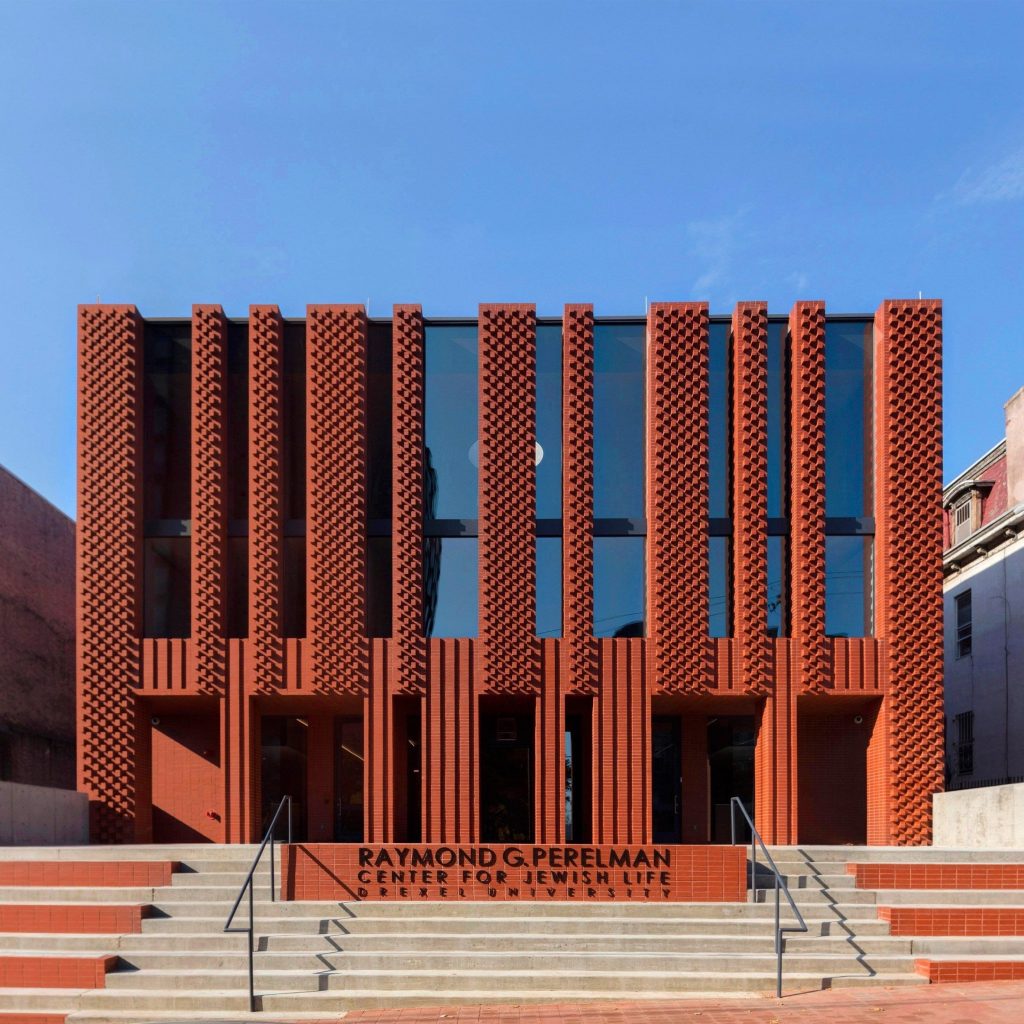

BRICK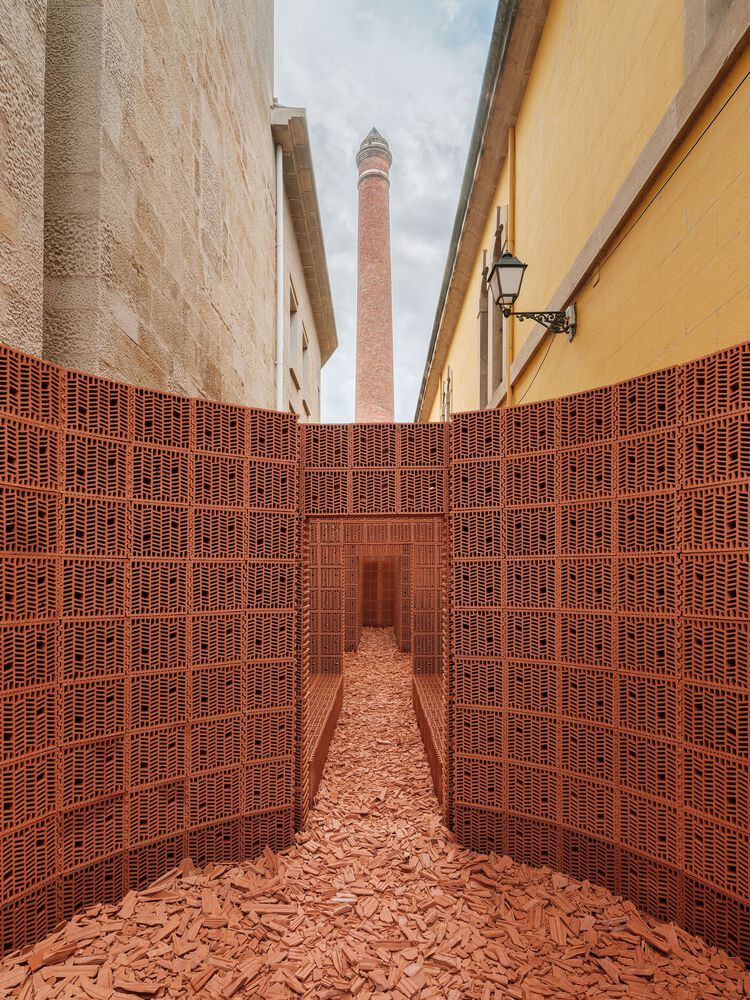 
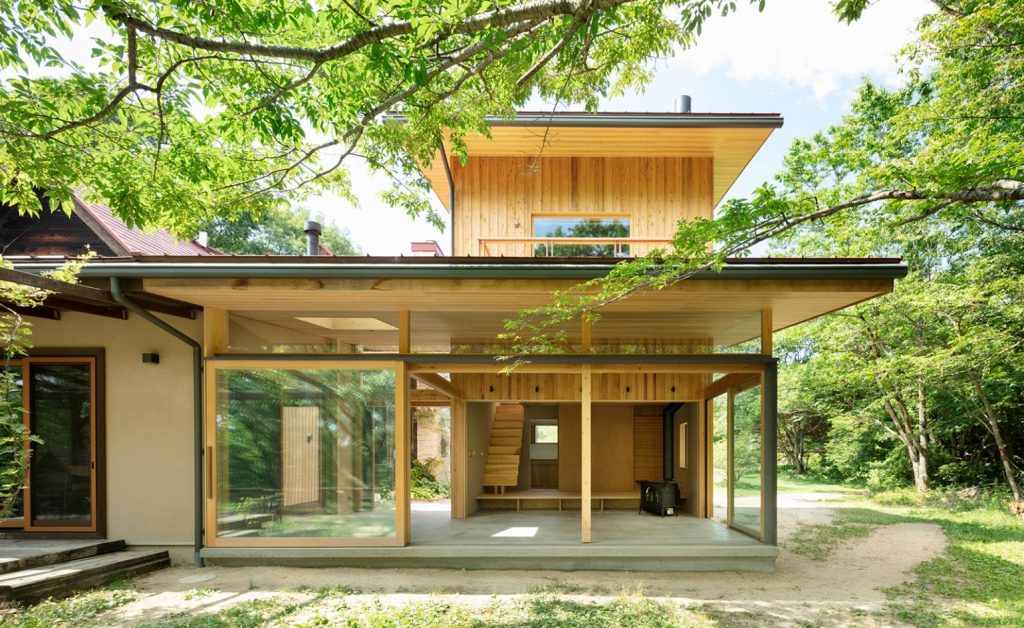

WOOD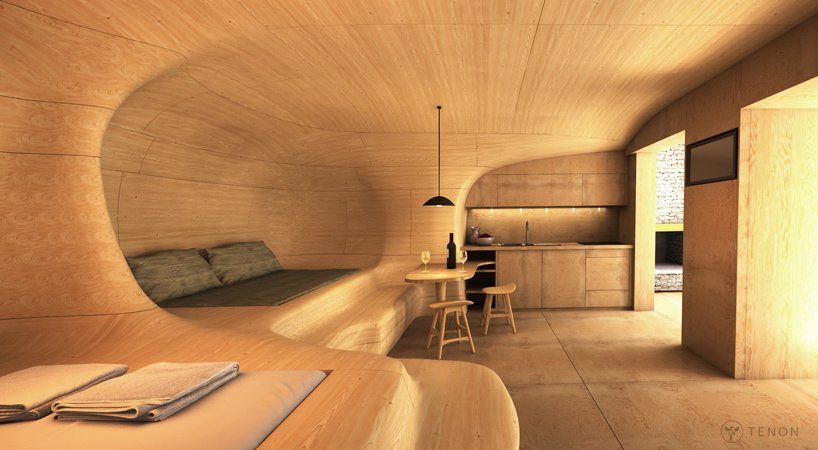 

STEEL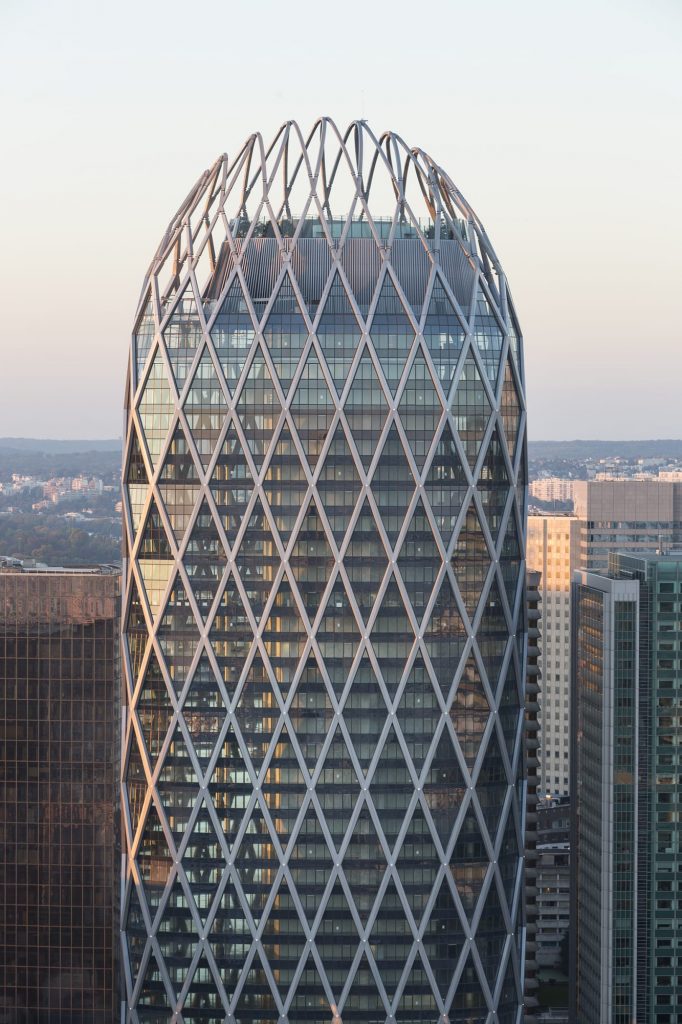 
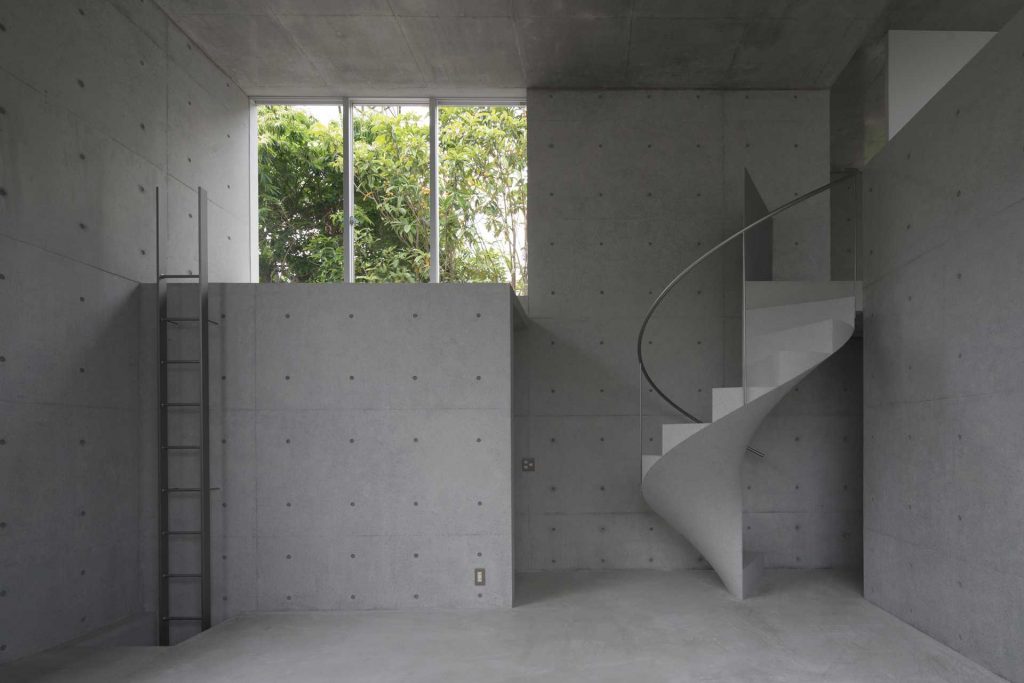

CONCRETE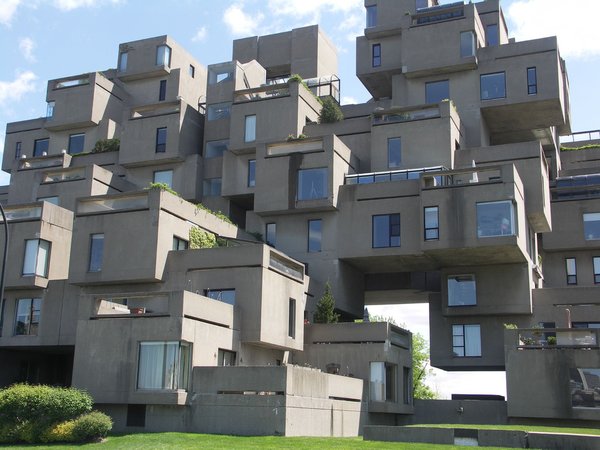 
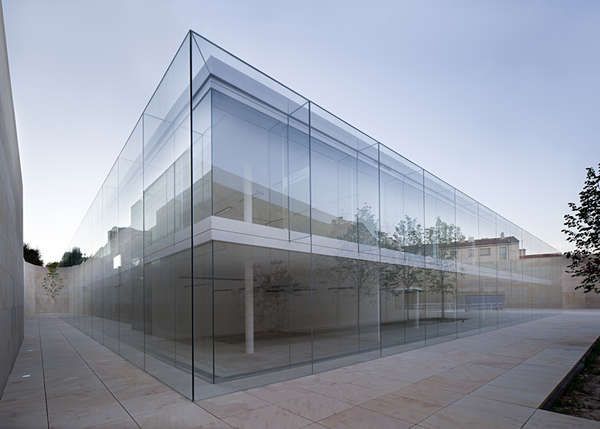

GLASS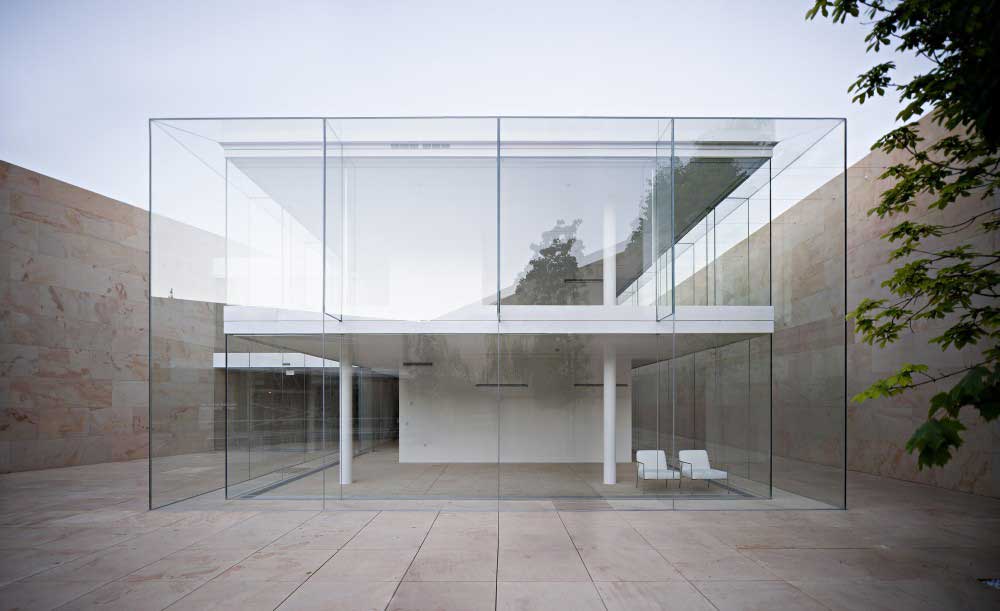 
TECHNOLOGY
+Roman construction
-arch and vault — covering
-walls — basic support
-concrete (arranged in a work by shutterings in vaults and domes and outer layers) —main material
inert strength + supports are thick and solid enough to resist rigidly
+Romanesque architecture
-barrel vault reinforced by transverse arches —roof
-groin vaults — new covering system (transverse ribs and formerets)
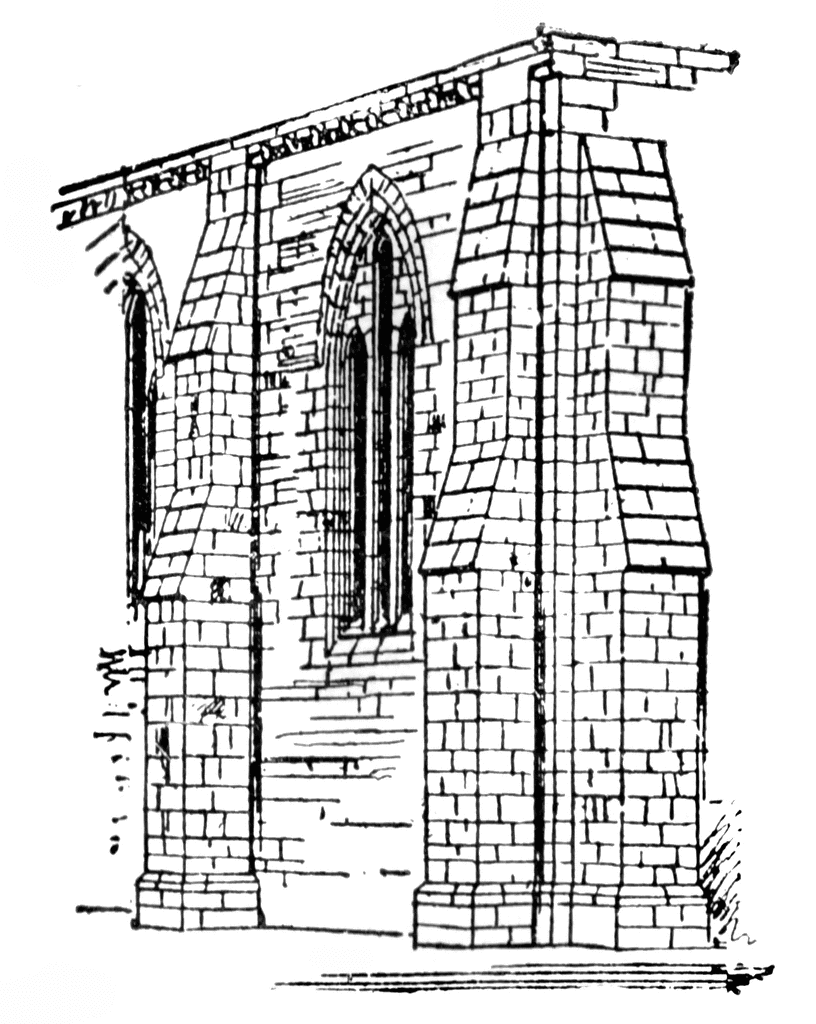
+Gothic architecture
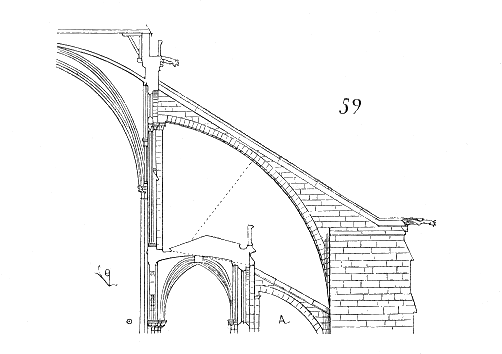
-pointed arch, the rib vault, the buttress, the flying buttress (arc-boutant), the pinnacles
-balancing forces
+Innovation
Computer Aided Design (CAD) 
Building Information Modeling (BIM)




